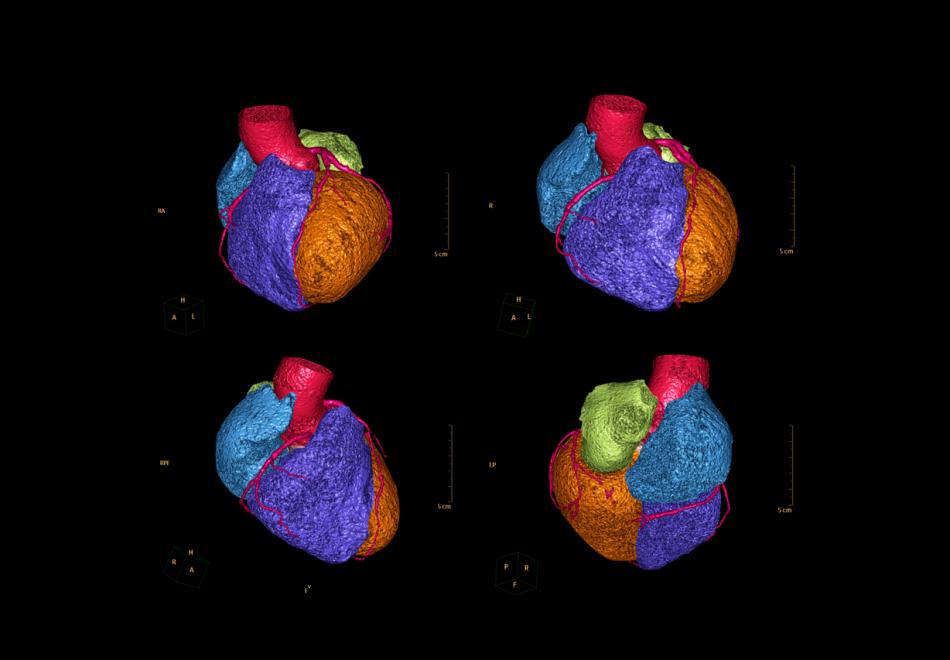
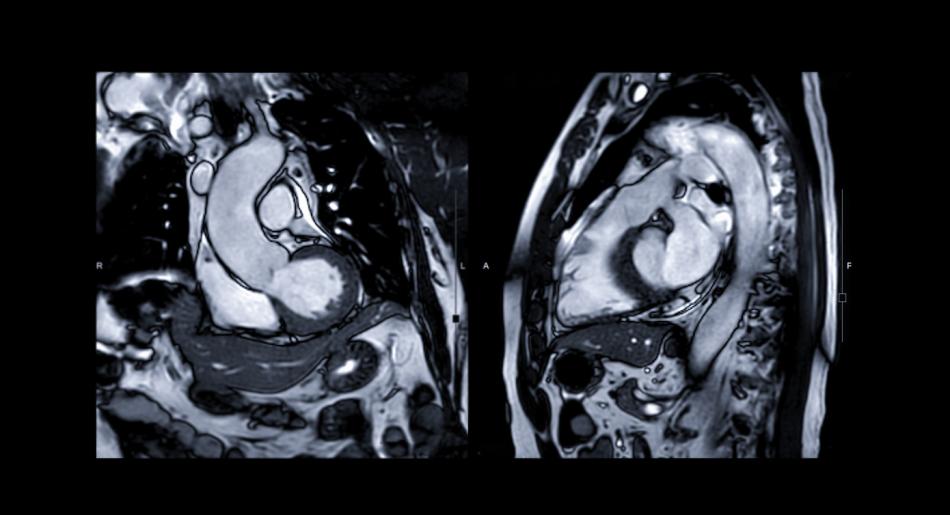
Common presenting symptoms:
Breathlessness; leg swelling (oedema); may present with palpitation / fainting on exercise
Overview:
Cardiomyopathy is a group of widely heterogeneous conditions with heart muscle abnormalities. They can be inherited with strong genetic predisposition; or acquired later in life from secondary causes. Heart muscle can be thickened (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) or the heart chamber can be “dilated and baggy” (dilated cardiomyopathy). Whenever cardiomyopathy is suspected, it is important to work out whether the heart muscle / chamber changes as an adaptation / maladaptation to pathophysiological stress, versus primary heart muscle pathologies affecting the muscle itself.
Thickened heart muscle can be caused by long-standing under-treated high blood pressure (hypertension) or undiagnosed valvular heart disease. It can also arise from infiltrative disease when abnormal protein or lipids are deposited within the muscle wall. Alternatively, particularly in those with history of palpitation or fainting on exercise, inheritable hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HCM) may be suspected.
Dilated heart chambers may also be caused by end-stage hypertensive / valvular heart disease; but it may equally be caused by a long list of biochemical / hormonal disturbance such as vitamin B / thiamine deficiency, thyroid disease; as well as chronic alcohol misuse / heart muscle injury from viral infection and toxin / post-partum cardiomyopathy, etc.
Expert evaluation of cardiomyopathy is important - as identification of potentially reversible causes could lead to reversal and heart muscle recovery. Likewise, for inheritable causes, it may need in-depth discussion about the merit of family screening.
How do we investigate?
If cardiomyopathy is suspected, in addition to a detailed history and specific blood tests, it is important to quantify heart muscle function, often with tissue characterisation. Our cardiologists will recommend one or more potential investigative tests such as:-
- Echocardiography to quantify heart and valve function
- Cardiac MRI to look for underlying heart muscle abnormality
- General and specific blood tests to exclude biochemical / hormonal reversible causes or infiltrative disease
What are the treatment options?
There is no single recommended treatment for this heterogeneous group of conditions collectively known as cardiomyopathy. Identification of potentially reversible causes is clearly important, with attempts to reverse biochemical / hormonal disturbance, which may lead to reversal and heart muscle recovery. Pharmacological therapy will maximise the chance of this heart muscle recovery. In some patients, special pacemaker device (Implantable Cardioverter Defribillator, ICD) implantation may be recommended to reduce risk of dangerous arrhythmia.